Fellow boiler enthusiasts, to another insightful discussion on the fascinating world of power generation. Today, we embark on a journey to unlock the untapped potential of CFB (circulating fluidized bed) boilers and explore how they distinguish themselves from their counterpart, fluidized bed boilers. If you’re a discerning buyer seeking the most efficient, environmentally friendly, and versatile solution for your energy needs, then this blog post is tailor-made for you.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the realm of CFB boilers, shedding light on their exceptional capabilities and highlighting the key points where they surpass traditional fluidized bed boilers. We’ll cover a range of topics that will help you make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the optimal boiler system for your specific requirements.
Key Operational Differences: Understanding the Working Principles of CFB and Fluidized Bed Boilers
Firstly, we’ll uncover the advantages that make CFB boilers stand out from the crowd, showcasing their superior performance and flexibility. From there, we’ll dive into the intricacies of their operation, understanding how they operate differently compared to fluidized bed boilers.
Fluidized bed boilers operate by introducing a bed of solid particles (typically sand or limestone) into the combustion chamber. Through the injection of air or gas, the particles are suspended and form a fluidized state. This fluidized bed acts as a medium for combustion, providing a large surface area for the fuel to react with the air, resulting in efficient heat transfer.
What is FFB (Fluidized bed) boilers?
Fluidized bed boilers operate by introducing a bed of solid particles (typically sand or limestone) into the combustion chamber. Through the injection of air or gas, the particles are suspended and form a fluidized state. This fluidized bed acts as a medium for combustion, providing a large surface area for the fuel to react with the air, resulting in efficient heat transfer.

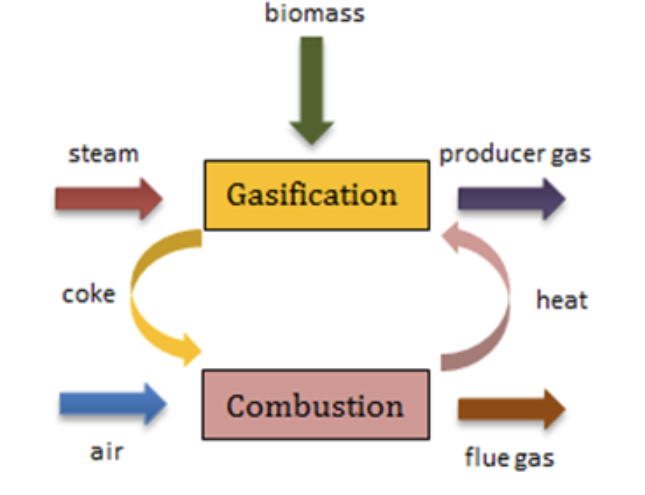
What is CFB (Circulating fluidized bed) boilers?
The circulating fluidized bed (CFB) is a type of Fluidized bed combustion that utilizes a recirculating loop for even greater efficiency of combustion.[1] while achieving lower emission of pollutants. Reports suggest that up to 95% of pollutants[2] can be absorbed before being emitted into the atmosphere. The technology is limited in scale however, due to its extensive use of limestone, and the fact that it produces waste byproducts.
[1]“Why fuel flexible CFBs are the future”. Power Engineering International. 2017-10-24. Retrieved 2020-06-11.
[2] Jump up to:a b [1] Archived 2013-10-29 at the Wayback Machine Circulating Fluidized Bed Technology, The Circulating Fluidized Bed Technology, 2010, Innovation and Information for sustainable living
Efficiency Comparison: Circulating Fluidized Bed (CFB) Boilers vs. Fluidized Bed Boilers
A crucial factor in any power generation process, will be our next focus. We’ll explore how CFB boilers excel in harnessing energy with enhanced efficiency, ensuring maximum utilization of resources and minimizing wastage.
When it comes to energy generation, efficiency plays a critical role in maximizing the utilization of resources and minimizing operational costs. We will delve into the efficiency comparison between circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers and fluidized bed boilers, examining the factors that differentiate the two technologies.
One of the primary advantages of CFB boilers over fluidized bed boilers is their ability to achieve higher combustion efficiency. CFB boilers employ a turbulent mixing zone created by the high-velocity circulating solids. This intense mixing promotes thorough fuel-air contact, facilitating complete combustion and reducing unburned carbon content in the ash. The result is enhanced combustion efficiency, ensuring optimal energy release and reducing energy losses associated with incomplete combustion.
Furthermore, CFB boilers excel in heat transfer efficiency. The circulating fluidized bed design allows for efficient heat transfer due to the turbulent mixing and high turbulence within the combustion chamber. This enhances the contact between the combustion gases and the heat exchange surfaces, facilitating effective heat transfer and maximizing the conversion of thermal energy into usable steam. The improved heat transfer efficiency of CFB boilers contributes to higher steam generation rates and overall thermal efficiency.
Fuel flexibility is another area where CFB boilers outshine fluidized bed boilers in terms of efficiency. CFB boilers can accommodate a wide range of fuel types, including low-quality fuels with high moisture content and varying particle sizes. This flexibility allows for efficient combustion even with challenging fuels, reducing energy losses associated with incomplete combustion or fuel inefficiencies. The ability to adapt to different fuel sources provides operational flexibility and helps optimize energy generation in diverse fuel scenarios.
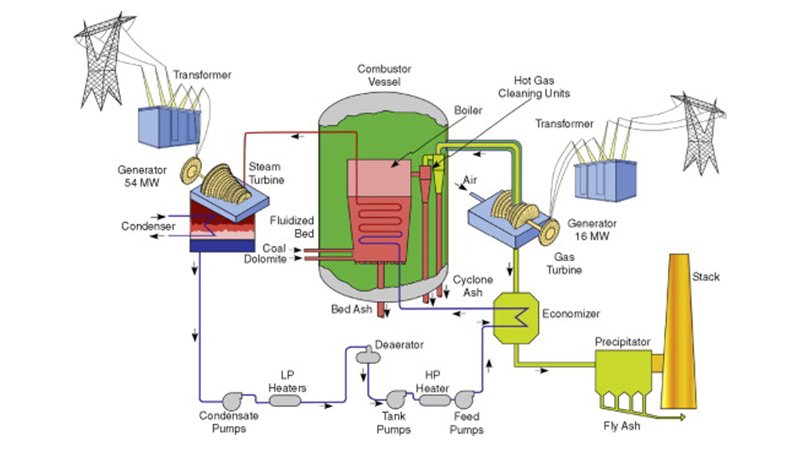
In addition to combustion and heat transfer efficiency, CFB boilers often incorporate advanced control systems. These systems optimize combustion parameters such as fuel-air ratios, bed temperature, and fluidization velocity, ensuring efficient energy generation. By maintaining optimal operating conditions, CFB boilers minimize energy losses and maximize overall efficiency. The advanced control mechanisms allow for precise adjustments, responding to varying load conditions and optimizing energy production.
It’s worth noting that fluidized bed boilers also offer their own advantages in terms of efficiency. They provide good fuel flexibility, allowing for efficient combustion of a variety of fuels. Fluidized bed boilers can handle different types of solid fuels, including biomass, coal, and even waste materials. Additionally, fluidized bed boilers exhibit excellent load-following capabilities, adjusting quickly to changing heat demands and ensuring stable combustion efficiency during varying load conditions.
In summary, while both CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers offer advantages in terms of efficiency, CFB boilers tend to outperform fluidized bed boilers in several key areas. The higher combustion efficiency, improved heat transfer efficiency, fuel flexibility, and advanced control systems of CFB boilers collectively contribute to their superior energy utilization and operational performance. However, it’s important to consider specific requirements and fuel characteristics when selecting the most suitable boiler technology for a given application.
Environmental Impact: Circulating Fluidized Bed (CFB) Boilers vs. Fluidized Bed Boilers
As responsible stewards of the environment, we cannot overlook the significance of emissions and pollution control. We’ll examine the stark contrast between CFB and fluidized bed boilers in terms of their environmental impact, demonstrating how CFB boilers offer cleaner and more sustainable solutions.
In an era where sustainability and environmental consciousness are paramount, the environmental impact of boiler systems is a crucial consideration. In this section, we will compare the environmental impact of circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers and fluidized bed boilers, shedding light on their respective contributions to a cleaner and greener future.
CFB boilers offer distinct advantages over fluidized bed boilers when it comes to emissions reduction. The turbulent mixing zone and intense combustion environment created by the high-velocity circulating solids in CFB boilers promote efficient and complete combustion. This results in lower emissions of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOx), compared to fluidized bed boilers. The ability to achieve higher combustion efficiency in CFB boilers significantly contributes to reducing their environmental footprint.
Moreover, CFB boilers are known for their excellent sulfur capture capability. The addition of limestone or other sulfur-absorbing agents to the circulating fluidized bed facilitates the removal of sulfur during combustion. This process, known as sulfur capture or desulfurization, effectively reduces sulfur dioxide emissions, helping to mitigate acid rain and the adverse effects associated with sulfur pollution.
In terms of nitrogen oxide emissions, CFB boilers have an inherent advantage over fluidized bed boilers. The high-velocity circulating solids and optimal combustion conditions in CFB boilers result in lower nitrogen oxide formation compared to fluidized bed boilers. This is achieved through a combination of factors, including lower combustion temperatures and reduced residence time of the fuel particles in the combustion chamber. The lower nitrogen oxide emissions contribute to improved air quality and reduce the environmental impact of energy generation.
Additionally, CFB boilers often incorporate advanced pollution control technologies, such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and flue gas desulfurization (FGD), to further reduce emissions. SCR systems help to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by converting them into harmless nitrogen and water through a catalytic process. FGD systems, as mentioned earlier, aid in sulfur capture and removal. The integration of these pollution control technologies demonstrates the commitment of CFB boiler manufacturers to mitigating environmental impact and ensuring compliance with stringent emission regulations.
While fluidized bed boilers also offer advantages in terms of environmental impact, CFB boilers generally surpass them in emission reduction and pollution control. However, it’s worth noting that the specific environmental performance of a boiler system depends on various factors, including fuel properties, combustion conditions, and the implementation of emission control technologies.
The environmental impact of boiler systems is a significant consideration, and CFB boilers have a distinct edge over fluidized bed boilers. Their ability to achieve efficient combustion, lower emissions of greenhouse gases and pollutants, and incorporation of advanced pollution control technologies position them as a greener and more sustainable option for energy generation. By choosing CFB boilers, we can contribute to a cleaner environment and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Application Areas: Circulating Fluidized Bed (CFB) Boilers vs. Fluidized Bed Boilers
We’ll turn our attention to the diverse applications of CFB boilers, identifying the industries and scenarios where their unique attributes shine brightest. By understanding their optimal usage, you’ll be empowered to make a choice that aligns perfectly with your specific needs.
Circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers and fluidized bed boilers are both versatile technologies that find applications in various industries. In this section, we will explore the different application areas where these boiler systems excel, highlighting their unique attributes and capabilities.
Power Generation
Both CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers have been widely adopted in the power generation sector. Their ability to efficiently combust a wide range of fuels, including coal, biomass, and waste materials, makes them suitable for diverse fuel scenarios. CFB boilers, with their superior fuel flexibility and efficiency, are often preferred for large-scale power plants. Fluidized bed boilers, on the other hand, are well-suited for smaller power generation units or combined heat and power (CHP) plants.
Industrial Processes
CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers play a crucial role in various industrial processes that require steam or heat. Industries such as paper and pulp, chemical, textile, and food processing benefit from the thermal energy generated by these boiler systems. The ability of CFB boilers to handle unconventional fuels and maintain stable combustion makes them suitable for industries where waste or biomass fuels are readily available. Fluidized bed boilers, with their compact size and efficient heat transfer, are often utilized in industries with smaller heat demands.

Co-generation and District Heating
CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers are employed in co-generation and district heating systems, where the simultaneous generation of electricity and heat is required. These boiler systems can efficiently produce both steam for electricity generation and hot water for heating applications. The flexibility of CFB boilers in utilizing different fuel sources and their ability to adjust to varying heat demands make them ideal for co-generation and district heating installations.
Waste-to-Energy
With the increasing focus on waste management and sustainable energy solutions, CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers are instrumental in waste-to-energy processes. These boiler systems can efficiently combust various waste materials, such as municipal solid waste, sewage sludge, and agricultural residues. The high combustion efficiency and effective control of emissions make CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers suitable for waste-to-energy plants, contributing to the reduction of landfill waste and the generation of renewable energy.
Biomass and Bioenergy
As the demand for renewable energy sources grows, CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers are extensively used in biomass and bioenergy applications. These boiler systems can effectively combust biomass fuels, such as wood chips, agricultural residues, and dedicated energy crops. CFB boilers, with their fuel flexibility and efficient combustion, are well-suited for large-scale biomass power plants. Fluidized bed boilers, with their compact design and efficient heat transfer, are often employed in smaller-scale biomass installations, including heat-only systems and combined heat and power (CHP) plants.
How to Buy the Right CFB Boiler?
Investing in a circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boiler requires careful consideration to ensure you choose the right system that meets your specific needs and delivers optimal performance.
Define Your Requirements
Begin by identifying your specific requirements and objectives.
Consider factors such as the desired steam or heat output, fuel type and availability, operating conditions, and any regulatory or environmental considerations. Clearly defining your requirements will help you narrow down the options and select a CFB boiler that aligns with your needs.

Assess Boiler Capacity
Determine the required capacity of the CFB boiler based on your heat or steam demand.
Consider both current and future requirements to ensure the boiler has sufficient capacity to handle potential expansion or increased demand. Consulting with a professional boiler engineer or supplier can help you accurately determine the required capacity for your application.
Evaluate Efficiency
Efficiency is a crucial aspect when selecting a CFB boiler.
Look for boilers that offer high combustion efficiency, heat transfer efficiency, and overall thermal efficiency. Consider the design features, such as the combustion system, heat exchange surfaces, and control mechanisms, that contribute to the boiler’s efficiency. Higher efficiency boilers can lead to significant energy savings and lower operating costs over the long term.
Fuel Flexibility
Assess the fuel flexibility of the CFB boiler.
Consider the types of fuels you have access to and whether the boiler can efficiently combust those fuels. CFB boilers are known for their ability to handle a wide range of fuels, including coal, biomass, and various waste materials. Ensure that the boiler’s fuel capabilities align with your fuel availability and requirements.
Quality and Reliability
Choose a reputable and reliable boiler manufacturer or supplier.
Look for companies with a proven track record in delivering high-quality CFB boilers and providing excellent after-sales support. Check customer reviews, references, and certifications to assess the manufacturer’s reputation for product quality and reliability. A well-built and reliable boiler will ensure uninterrupted operation and minimize downtime.
Emission Compliance
Consider the environmental impact and regulatory compliance of the CFB boiler.
Ensure that the boiler meets local emission standards and regulations for pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter. Look for boilers that incorporate advanced emission control technologies to minimize environmental impact and ensure compliance with stringent regulations.
Maintenance and Service
Evaluate the availability of maintenance and service support for the CFB boiler.
A reliable supplier should offer comprehensive maintenance plans, spare parts availability, and responsive customer support. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the boiler operating efficiently and to extend its lifespan.
Cost Considerations
While price is an important factor, it should not be the sole determining factor in your decision.
Consider the overall lifecycle cost of the boiler, including initial investment, operating costs, maintenance, and potential fuel savings. A higher upfront investment in a more efficient and reliable boiler can result in significant long-term cost savings.
In conclusion, buying the right CFB boiler requires a thorough understanding of your requirements, careful evaluation of capacity, efficiency, fuel flexibility, quality, emission compliance, maintenance and service support, and cost considerations. By considering these factors and working with reputable suppliers, you can select a CFB boiler that meets your needs, ensures optimal performance, and delivers long-term value for your investment.
CFB boilers and fluidized bed boilers find application in a wide range of industries and processes. Their versatility, fuel flexibility, and efficiency make them suitable for power generation, industrial processes, co-generation, district heating, waste-to-energy, and biomass and bioenergy applications. By understanding the unique attributes and strengths of each technology, industries can choose the most appropriate boiler system to meet their specific needs and contribute to efficient and sustainable energy generation.
Buy CFB boilerS from DHB Boiler
Ready to Harness the Power of CFB Boilers? Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and find the perfect CFB boiler solution for your energy needs.