We will embark on a journey to uncover the untapped potential of water-cooled walls and how they can truly elevate your boiler system to new heights of efficiency and performance.
In today’s fast-paced and energy-conscious world, optimizing boiler operations is more crucial than ever. That’s where water-cooled walls come into play. These cutting-edge solutions have captured the attention of industry experts and forward-thinking buyers alike, providing a game-changing approach to achieving unparalleled efficiency and sustainability in boiler systems.
How Water-Cooled Walls Enhance Boiler Efficiency and Performance
Water-cooled walls are a groundbreaking technology that significantly enhances boiler efficiency and performance. By optimizing heat transfer through a network of water-filled tubes, these structures improve the absorption of heat generated during combustion, resulting in reduced energy consumption, lower operating costs, and minimized environmental impact. Water-cooled walls promote better temperature control, extend equipment lifespan, and are suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Their implementation leads to significant cost savings and contributes to a greener and more sustainable operation. Selecting the right water-cooled wall solution for your boiler system is crucial, and consulting with experts is recommended. In summary, water-cooled walls are a game-changer for the boiler industry, elevating systems to unprecedented levels of efficiency and sustainability.
The Science Behind Water-Cooled Walls: How They Work and Why They Matter
What is water-cooled walls?
Water-cooled walls panels are the main heating surface of boilers, composed of numbers of rows of steel tubes, arranged around the boiler corner. Inside is the flowing water or steam, and the outside accepts the heat of the flame in the furnace of the boiler, mainly absorbing the radiation heat of the high temperature combustion products in the furnace. The working fluid rises in it and evaporates by heat.
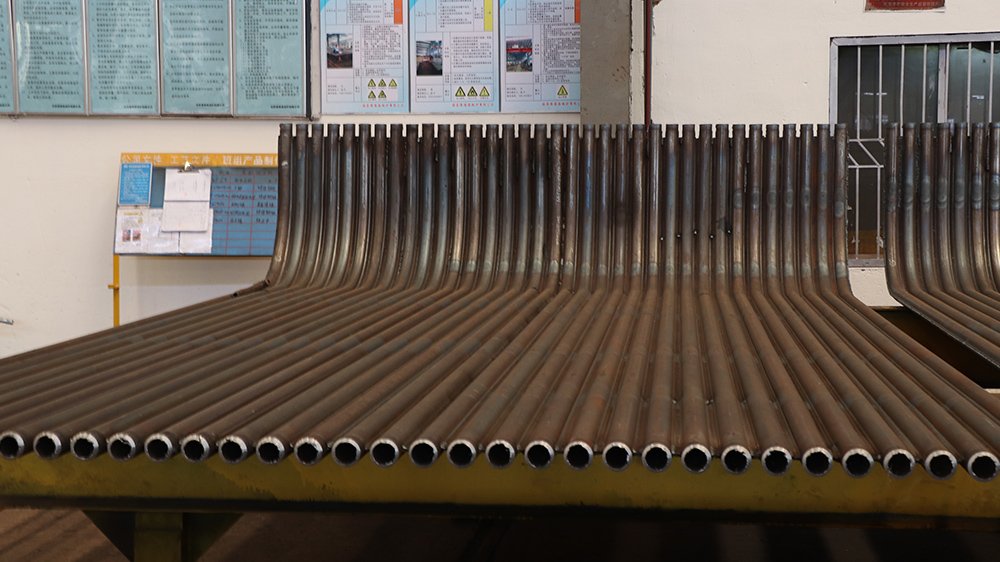

Water-cooled walls are a technological marvel that operates on a simple yet effective principle: optimizing heat transfer to enhance boiler performance. Understanding the science behind water-cooled walls is essential to appreciate their significance in the realm of boiler systems. These innovative structures work by utilizing a network of water-filled tubes strategically placed in direct contact with the heat source, be it the combustion process or the flue gases. By facilitating direct contact between the water and the heat, water-cooled walls enable efficient heat transfer, leading to improved boiler efficiency and overall system performance.
The heart of water-cooled walls lies in their ability to absorb heat. Traditional boiler walls often struggle to efficiently transfer heat from the combustion process to the surrounding water or steam, leading to energy loss and reduced efficiency. Water-cooled walls address this issue by employing a configuration that maximizes the heat absorption capacity. The water-filled tubes act as conduits, allowing the transfer of heat from the combustion chamber to the water, where it is effectively captured and utilized.
The importance of efficient heat transfer cannot be overstated. By optimizing heat absorption through water-cooled walls, boilers can achieve higher thermal efficiencies. This means that a larger proportion of the heat generated during combustion is effectively utilized to produce steam or hot water, while minimizing wasteful energy losses. As a result, boiler systems with water-cooled walls consume less fuel for the same output, leading to significant energy savings and reduced operational costs.
But why does efficient heat transfer matter? The answer lies in the impact it has on the overall performance and sustainability of boiler systems. When heat is transferred more effectively, boilers can operate at higher efficiencies, which reduces the consumption of fossil fuels and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. This not only contributes to a more environmentally friendly operation but also aligns with the increasing focus on energy conservation and sustainability.
Water-cooled walls also play a crucial role in maintaining temperature control within the boiler system. By efficiently removing heat from the combustion process, they help regulate and stabilize the temperature distribution, preventing the formation of hotspots and minimizing thermal stress on the boiler components. This leads to improved system reliability, reduced maintenance requirements, and an extended lifespan for the equipment.
Furthermore, the design and configuration of water-cooled walls can be tailored to suit different boiler types and applications. Factors such as wall material, tube arrangement, and water flow rate can be optimized to ensure maximum heat transfer efficiency. Consulting with experts and manufacturers in the field is essential to select the most suitable water wall solution that aligns with the specific requirements and operating conditions of your boiler system.
The science behind water-cooled walls revolves around their ability to facilitate efficient heat transfer, resulting in improved boiler performance and sustainability. By maximizing heat absorption, these innovative structures enhance thermal efficiencies, reduce energy consumption, and lower operational costs. They contribute to temperature control, system reliability, and prolonged equipment lifespan. Understanding the science behind water walls is crucial for realizing their potential and making informed decisions when implementing them in your boiler system.
Different Types of Water-Cooled Walls: Exploring Your Options
When it comes to water walls, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. These innovative structures come in different types, each offering unique features and advantages. Exploring the various options available is crucial to select the right water wall that aligns with your specific boiler system requirements. Let’s delve into the different types of water walls and their distinguishing characteristics.
Tube and Header Design
One common type of water-cooled wall is the tube and header design. In this configuration, a series of tubes are connected to headers at the top and bottom of the wall. The headers distribute the water evenly across the tubes, ensuring efficient heat transfer and uniform cooling. Tube and header designs are versatile, widely used, and suitable for a range of boiler applications.
According to the structure type, there are mainly light tube water wall, membrane water wall and pin type water wall three types.
Light Tube Water-cooled Wall
The light tube water-cooled wall consists of a whole row of seamless steel tubes, the structure is the simplest, widely used in small and medium capacity boilers.
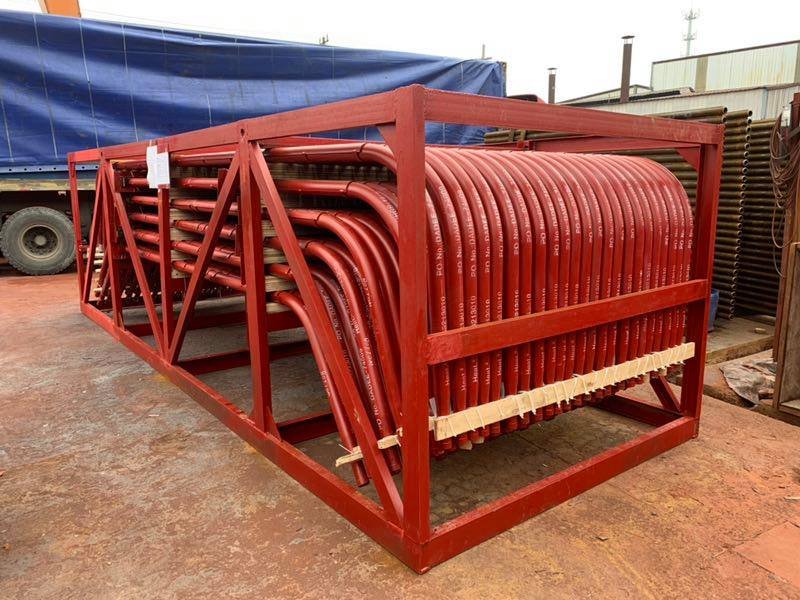
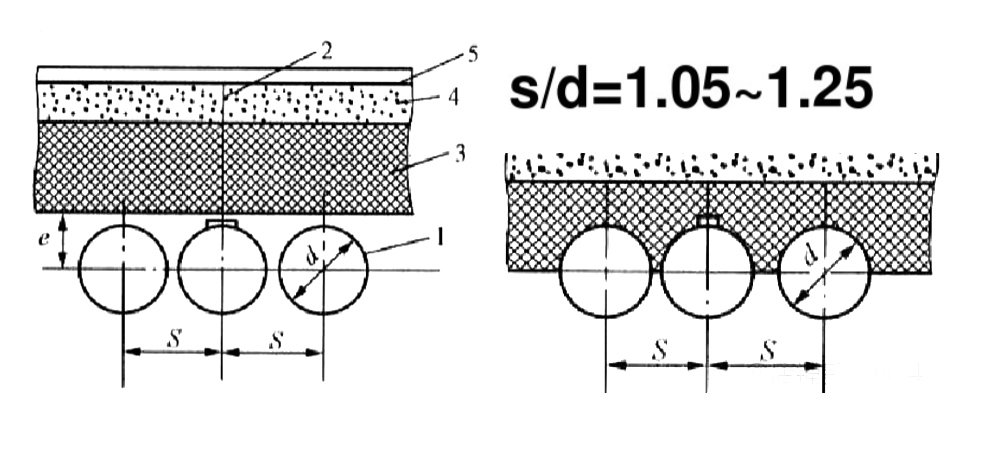

Membrane Wall
Membrane water-cooled wall is a number of rolled water wall fins welded together with spot welding, making a sealed combination of heating surface, not only to improve the gas tightness of the chamber, reduce air leakage, but also to better protect the furnace wall, so that the weight of the wall is reduced, the structure is simplified. Large capacity, high temperature and high-pressure boilers mostly use membrane water wall.
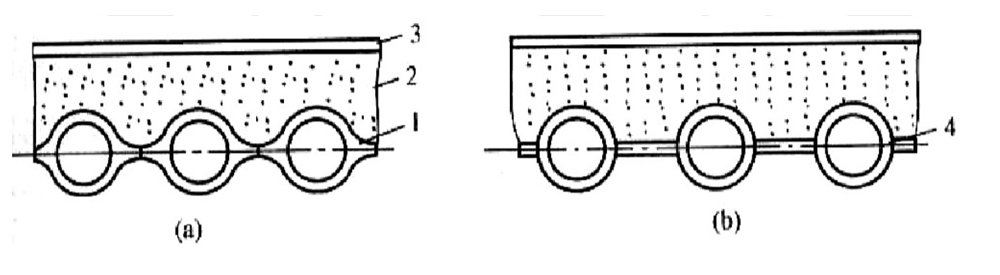

Pin water-cooled wall
Pin water-cooled wall is in the wall tube welded many 20 ~ 25mm long, 6 ~ 12mm diameter pin, and then coated with chrome ore refractory plastic, in order to reduce the water wall of the part of the heat absorption, improve the temperature of the combustion zone, for the occasion of fuel ignition is particularly difficult or some liquid slagging furnace.
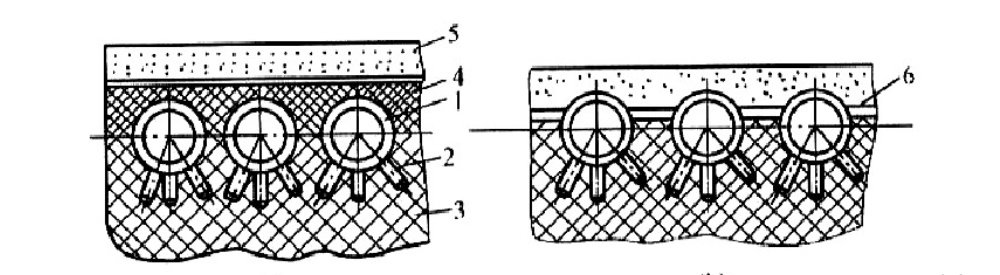

According to the arrangement of parts, there are attached to the wall water-cooled wall and partition wall water wall (that is, double-sided heat) of two kinds.
. Most of the water-cooled wall attached to the wall is partially embedded in the inner wall surface of the furnace wall, single-sided heat absorption.
. Wall water wall is mostly installed in the middle of the large boiler chamber, the entire chamber separated into two independent parts, two-sided heat.
DHB’s boiler has various models of boiler water-cooled wall, the following are the parameters of the hot models of DHB boiler water wall:
Specifications:
| Name | Membrane water panel |
| Material | Carbon steel,Alloy steel,etc. |
| Tube size | Φ38 – 76 mm, Customization |
| Standard | ISO , ASME |
| Model | Studded |
| Dimension | Customization |
| Manufacturing process | Material→Ingot → Hot/Cold-Rolling→ Heat treatment (Normalizing+ tempering) → Inspection →Polishing→Tube joint welding→Assembly →Welding →Inspection→Heat treatment→Hydraulic pressure test→Painting→ Packaging |
| Installation location | Around the boiler combustion chamber |
Selecting the right water wall type for your boiler system requires careful consideration of factors such as operating conditions, fuel type, boiler size, and efficiency requirements. Consulting with experienced engineers and manufacturers is crucial to assess your needs accurately and determine the most suitable water-cooled wall type that will maximize performance and longevity while meeting your specific application requirements.
By exploring the different types of water walls and understanding their unique characteristics, you can make an informed decision when selecting the optimal solution for your boiler system. Each type brings its own advantages and considerations, allowing you to tailor your choice to match your operational needs. Remember, the right water wall can significantly enhance efficiency, performance, and longevity, ensuring your boiler system operates at its best.
Water-Cooled Walls vs. Traditional Boiler Walls: A Comparative Analysis
Water-cooled walls have emerged as a groundbreaking technology that revolutionizes the world of boiler systems. To truly appreciate their significance, it’s essential to compare them to traditional boiler walls and understand the key differences. In this comparative analysis, we will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of water walls and traditional boiler walls, shedding light on why water walls have gained prominence in recent years.
One of the fundamental distinctions between water walls and traditional boiler walls lies in their heat transfer capabilities. Traditional boiler walls typically rely on radiation and convection for heat transfer, which can be less efficient compared to water walls. Water-cooled walls, on the other hand, leverage direct contact between water-filled tubes and the heat source, maximizing heat transfer efficiency. This results in improved boiler performance, higher thermal efficiencies, and reduced energy consumption.
Efficiency and energy savings are significant advantages of water walls over traditional boiler walls. The enhanced heat transfer of water walls allows for more effective heat absorption, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower operating costs. In contrast, traditional boiler walls may experience higher energy losses, as a portion of the heat generated during combustion is not efficiently captured and utilized.
Another crucial factor to consider is temperature control. Water walls excel in maintaining uniform temperature distribution within the boiler system, thanks to their efficient heat removal capabilities. This helps prevent hotspots and minimizes thermal stress on the boiler components, enhancing system reliability and extending equipment lifespan. Traditional boiler walls may be more susceptible to temperature variations, which can lead to uneven heat distribution and potential equipment damage.
When it comes to high-pressure and high-temperature applications, water walls offer distinct advantages over traditional boiler walls. Their robust construction and ability to withstand extreme conditions make them well-suited for demanding environments, such as power plants and industrial facilities. Traditional boiler walls may face challenges in managing thermal stress and maintaining structural integrity under these rigorous operating conditions.
Maintenance and longevity are additional factors to consider. Water walls typically require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure proper functioning and prevent issues such as tube fouling or corrosion. Traditional boiler walls may also require maintenance, but the specific requirements can vary depending on the design and materials used. It’s crucial to consider the long-term maintenance implications when comparing the two types of walls.
While water walls offer numerous advantages, it’s important to acknowledge that their installation and integration can be more complex compared to traditional boiler walls. The design and configuration of water-cooled walls need to be carefully tailored to the specific boiler system, operating conditions, and other factors. Expert engineering and installation are crucial to ensure optimal performance and functionality.
In summary, the comparative analysis between water walls and traditional boiler walls reveals the transformative advantages of water-cooled walls. Their enhanced heat transfer capabilities, improved efficiency, better temperature control, suitability for high-pressure applications, and extended equipment lifespan make them an appealing choice for modern boiler systems. While traditional boiler walls have their merits, water walls have emerged as a game-changer in optimizing performance, reducing energy consumption, and ensuring sustainable operation. Investing in water-cooled walls can unlock new levels of efficiency and effectiveness in boiler systems, revolutionizing the way we approach heating and power generation.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Boiler Systems with Water-Cooled Walls
| Project Name | Product(s) Name |
| Hongkong Nanya Power Plant | Water wall, superheater (HR3C/TP347HFG/T91) |
| Australia RCR Energy/FM Boiler Furnace Panels | Water wall |
| New Zealand RCR(FM Boiler Furnace Panels) | Water wall |
| Vietnam PHA LAI Power Plant | Water wall |
FAQ
Here are some common questions and answers related to water walls and their impact on boiler systems:
- What are water-cooled walls?
Water-cooled walls are structures within a boiler system that utilize a network of water-filled tubes in direct contact with the heat source to optimize heat transfer and enhance boiler efficiency. - How do water-cooled walls improve boiler efficiency?
Water-cooled walls improve boiler efficiency by maximizing heat transfer from the combustion process to the water, ensuring more effective heat absorption and reducing energy losses. - What are the benefits of water-cooled walls over traditional boiler walls?
Compared to traditional boiler walls, water-cooled walls offer advantages such as higher thermal efficiencies, reduced fuel consumption, better temperature control, extended equipment lifespan, and suitability for high-pressure applications. - Can water-cooled walls be retrofitted into existing boiler systems?
Yes, water-cooled walls can be retrofitted into existing boiler systems, but it requires careful engineering and design considerations to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. - Are water-cooled walls more expensive to install and maintain?
The installation and maintenance costs of water-cooled walls can be higher compared to traditional boiler walls. However, the long-term energy savings and improved efficiency can offset these initial costs over the lifespan of the system. - Do water-cooled walls require special maintenance?
Water-cooled walls may require regular inspection and maintenance to prevent issues such as tube fouling or corrosion. Proper water treatment and monitoring are crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. - Can water-cooled walls accommodate different boiler types and sizes?
Yes, water-cooled walls can be designed and configured to accommodate various boiler types and sizes. Consulting with experts is important to ensure the best fit for your specific boiler system. - Are water-cooled walls environmentally friendly?
Yes, water-cooled walls contribute to a greener and more sustainable operation by improving boiler efficiency and reducing fuel consumption, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions. - How do water-cooled walls impact system reliability?
Water-cooled walls promote better temperature control, preventing hotspots and reducing thermal stress on boiler components. This leads to improved system reliability, reduced maintenance requirements, and extended equipment lifespan. - Can water-cooled walls be used in both industrial and residential applications?
Water-cooled walls are versatile and can be used in various applications, including both industrial and residential settings, depending on the specific requirements and operating conditions of the boiler system.
Don’t let your boiler system lag behind. Take the first step towards improved efficiency and performance by exploring our range of water-cooled walls.








